My first experience with Lemmy was thinking that the UI was beautiful, and lemmy.ml (the first instance I looked at) was asking people not to join because they already had 1500 users and were struggling to scale.
1500 users just doesn’t seem like much, it seems like the type of load you could handle with a Raspberry Pi in a dusty corner.
Are the Lemmy servers struggling to scale because of the federation process / protocols?
Maybe I underestimate how much compute goes into hosting user generated content? Users generate very little text, but uploading pictures takes more space. Users are generating millions of bytes of content and it’s overloading computers that can handle billions of bytes with ease, what happened? Am I missing something here?
Or maybe the code is just inefficient?
Which brings me to the title’s question: Does Lemmy benefit from using Rust? None of the problems I can imagine are related to code execution speed.
If the federation process and protocols are inefficient, then everything is being built on sand. Popular protocols are hard to change. How often does the HTTP protocol change? Never. The language used for the code doesn’t matter in this case.
If the code is just inefficient, well, inefficient Rust is probably slower than efficient Python or JavaScript. Could the complexity of Rust have pushed the devs towards a simpler but less efficient solution that ends up being slower than garbage collected languages? I’m sure this has happened before, but I don’t know anything about the Lemmy code.
Or, again, maybe I’m just underestimating the amount of compute required to support 1500 users sharing a little bit of text and a few images?
The numbers are a little higher than you mention (currently ~3.2k active users). The server isn’t very powerful either, it’s now running on a dedicated server with 6 cores/12 threads and 32 gb ram. Other public instances are using larger servers, such as lemmy.world running on a AMD EPYC 7502P 32 Cores “Rome” CPU and 128GB RAM or sh.itjust.works running on 24 cores and 64GB of RAM. Without running one of these larger instances, I cannot tell what the bottleneck is.
The issues I’ve heard with federation are currently how ActivityPub is implemented, and possibly the fact all upvotes are federated individually. This means every upvote causes a federation queue to be built, and with a ton of users this would pile up fast. Multiply this by all the instances an instance is connected to and you have an exponential increase in requests. ActivityPub is the same protocol used by other federated servers, including Mastodon which had growing pains but appears to be running large instances smoothly now.
Other than that, websockets seem to be a big issue, but is being resolved in 0.18. It also appears every connected user gets all the information being federated, which is the cause for the spam of posts being prepended to the top of the feed. I wouldn’t be surprised if people are already botting content scrapers/posters as well, which might cause a flood of new content which has to get federated which causes queues to back up; this is mostly speculation though.
As it goes with development, generally you focus on feature sets first. Optimization comes once you reach a point a code-freeze makes sense, then you can work on speeding things up without new features breaking stuff. This might be an issue for new users temporarily, but this project wasn’t expecting a sudden increase in demand. This is a great way to show where inefficiencies are and improve performance is though. I have no doubt these will be resolved in a timely manner.
My personal node seems to use minimal resources, not having even registered compared to my other services. Looking at the process manager the postgres/lemmy backend/frontend use ~250MB of RAM.
For now, staying off lemmy.ml and moving communities to other instances is probably best. The use case of large instances anywhere near the scale of reddit wasn’t the goal of the project until reddit users sought alternatives. We can’t expect to show up here and demand it work how we want without a little patience and contributing.
Yup was just typing a comment to basically this effect. Federation adds a ton of overhead – you can still do things fairly efficiently, but every interaction having to fan out to (and fan in from!) many servers instead of like a single RDBMS is gonna cost you.
In all likelihood the code is not as efficient as it could be, but usually you get time to work those out gradually. A giant influx of users quickly turns “TODO: fix in the next six months” into “Oh god the servers are melting fuck fuck.”
That said, assuming the devs can get over this hump, I suspect using a compiled language will pay off long-term. Sure things will still be primarily IO-bound, but making things less CPU-bound is usually a good thing.
For some illustrative examples: Mastodon is in Ruby and hits dumb scaling limitations far more often than other fedi microblogs. Pleroma/Akkoma are Elixir (and BEAM is super well optimized for fast message passing/scaling/IO), Calckey (primarily Typescript) is moving some code to Rust, GoToSocial (Golang) is able to run in a fraction of the resources of Mastodon. The admins of one of the bigger tech instances recently announced they’re basically giving up on administrating Mastodon and are instead going to write a new server from scratch in a compiled language because it’s easier for them than scaling a Rails monolith.
TL;DR everything is IO-bound til it’s not.
I’m pretty sure the fediverse needs a new kind of node at some point. If we assume, that almost every larger instance is connected to almost every other larger instance directly, then there’s a ton of duplicated and very small messages.
There needs to be some kind of hub in-between to aggregate and route this avalanche. Especially if, like you wrote, every upvote is a message, the overhead (I/O, unmarshalling, etc) is huge.
You mean like centralizing the fediverse? Who hosts the hub? Who maintains it? In which country? Who pays for it?
Not a single hub, multiple ones.
Anyone can host a hub, federated instances can negotiate the intersection of hubs they both trust and then send traffic that way. That could mean, a single comment might be sent to, say, five hubs and each hub then forwards to 50 instances or so.
Since the hubs are rather simple, they can scale very easily and via cryptographic ratchets, all instances can make sure, they received the correct messages.
Hmm. Does the federation protocol only send information directly between servers, by that I mean that when something happens on A, does it send it to all other federated servers by itself?
If you could just proxy messages through other servers it would be an improvement. Essentially every instance would also be a hub. If you’re an instance A, connected to B and C, when B send you something you pass it onto C, instead of having C communicate with B directly.
In order to prevent spam you’d need whitelisting for the instances which you will act as a proxy for, and messages will have to be signed. Also, some protocol to discover the topology surrounding your server would be neat for optimizing delivery.
O(n*n) isn’t really scalable, so you either
a - have a small number of nodes total
b - have a small number of hubs with a larger number of leaf nodes.
Either way, there’s going to be some nodes that become more influential than others.
This is kinda how Usenet worked (well, still does). Rather than n*n federated connections, smaller providers tend to federate with central hubs that form backbones.
I think it makes sense for the fediverse as well.
Well said. Thanks for sharing your experience and those insightful links.
I can’t imagine what possessed them to use websockets other than “gee whiz websockets.”
Probably the same appeal as rust though: gee whiz.
What specs are you running your instance on?
An old Chromebox G1 (i7-4600U and 8GB of ram) with a 128GB internal NGFF and external 1TB NVMe. It’s by no means powerful or expensive hardware. I’m also only receiving federated posts for my subscribed communities, and sending out these comments I write so it’s a lot lower workload than the larger instances.
Hosting a personal instance is the direction I want to go. That’ll be a winter project, though. It’s fishing/swimming/rowing/woodworking season now :)
Are there any general tips or hidden dangers you can share? Or is it as straightforward as just putting my nose into documentation and playing around a bit?
Right now there appears to be no more danger than hosting anything else. I run my services behind a reverse proxy to insulate my home LAN from the wider internet, but hooking anything up to the internet comes with potential dangers.
I personally wrote a helm chart for kubernetes to host the service, and a few more can be found here. I have some work to do yet on the helm chart but it closely mirrors the docker-compose file provided by the developers. Deployment of an instance should be a lot easier soon, with all the increased interest and contributions.
I would say that it’s extremely unlikely.
Websites in general are never limited by raw code execution, they are mostly limited by IO. Be that disk IO as files are read and written, database IO as you need to execute complex queries to gather all the data to build the user timeline, and network IO to transfer data to and from the user. For decentralized social media like Kbin or Lemmy its even more IO limited as each instance needs to go back and forth to other instances to keep up-to-date data.
Websites usually benefit much more from caching and in-memory databases to keep frequently used data in fast storage.
This is why simple, high level, object oriented, garbage collected languages have become so common. All the CPU performance penalties they incur don’t actually affect the website performance.
Not relevant to lemmy (yet), but this does break down a bit at very large scales. (Source: am infra eng at YouTube.)
System architecture (particularly storage) is certainly by far the largest contributor to web performance, but the language of choice and its execution environment can matter. It’s not so important when it’s the difference between using 51% and 50% of some server’s CPU or serving requests in 101 vs 100 ms, but when it’s the difference between running 5100 and 5000 servers or blocking threads for 101 vs 100 CPU-hours per second, you’ll feel it.
Languages also build up cultures and ecosystems surrounding them that can lend themselves to certain architectural decisions that might not be beneficial. I think one of the major reasons they migrated the YouTube backend to C++ isn’t really anything to do with the core languages themselves, but the fact that existing C++ libraries tend to be way more optimized than their Python equivalents, so we wouldn’t have to invest as much in developing more efficient libraries.
It is fairly relevant to lemmy as is. Quite a few instances have ram constraints and are hitting swap. Consider how much worse it would be in python.
Currently most of the issues are architectural and can be fixed with tweaking how certain things are done (i.e., image hosting on an object store instead of locally).
In lemmy’s case, my perusal of the DB didn’t really suggest that the queries would be that complex and I suspect that moving it to a higher performance NoSQL DB might be possible, but I’d have to take a look at a few more queries to be sure.
I wonder if this could be made to work with Aerospike Community Edition…
Obviously it could be more effort than it’s worth though.
The issues I’ve seen more are around images. Hosting the images on an object store (cloudflare r2, s3) and linking there would reduce a lot of federation bandwidth, as that’s probably cause higher ram/swap usage too.
pict-rs supports storing in object stores, but when getting/serving images, it still serves through the instance as the bottleneck IIRC. That would do quite a bit to free up some resources and lower overall IO needed by the server.
There’s no need to migrate the database, that shouldn’t be an issue at this size. Caching should be implemented as another comment suggested.
Would you be so kind as to recommend some resources about caching? I’ve read the basics, but have yet to dive deep on it
The basic idea is to keep data as close to the processor as possible, so with a database that means storing the result of commonly used queries in memory.
Good resources.
Oh shit does lemmy not have response caching? Yeah, that’s gonna be an issue pretty soon.
That’s correct. I wonder if YouTube still uses Python to this day.
Not saying there isn’t a difference in language performance, but for most world problems the architecture and algorithms matter more than the language for performance. Unless you’re in a very constrained environment such as lower end smartphones or embedded systems.
I wonder if YouTube still uses Python to this day
We do not.
Also this makes you think (assuming it’s true lol): https://www.reddit.com/r/Lemmy/comments/14h965f/comment/jpdemet
It could be the devs just like programming in Rust. It’s a nice language lol
I know I do. ¯\_(ツ)_/¯
I think the devs openly stated they aren’t backend bods and asked for help optimising the database as a priority. There’s a bit of work going on on github to sort that out I think. Anyone reading this who can optimise postgresql or contribute to a database agnostic retool should probably speak to the devs as I imagine you’d be welcome.
I wish I could help so much but I doubt they’re going to retool into .net haha.
Which is fine. If they wanted to learn Rust and wrote inefficient code, good for them. I appreciate their efforts. Rust can certainly be beaten into shape and perform well enough in the end.
Rust itself or the way the Rust logic is implemented is not the bottleneck. Like most decent web applications the bottleneck is the database and how the decentralized protocols themselves are reconciled there.
Scaling massive amounts of records like Lemmy has been forced to is almost always IO bound at the database level even when a web service is centralized; this is much more difficult in federated architectures. This is why “NoSQL” databases have increased in popularity, but they are also not a magic bullet as there are major ACID trade offs one needs to consider.
NoSQL databases are no silver bullet and the costs of ACID are usually exaggerated (plus most NoSQL databases actually implement ACID anyway). NoSQL databases and SQL databases often have similar performance characteristics since most of the technology is typically the same under the hood.
Plus from my experience as a database consultant: databases are rarely IO bound, NoSQL or SQL unless you have a strange workload. Most time for query execution is usually spent waiting on loads or executing CPU instructions, not waiting on disk IO.
One benefit of using rust for webservers in general is that it’s possible to have a consistently lower latency compared to GCd langues: discord mentions this in their article about migrating to rust from go: https://discord.com/blog/why-discord-is-switching-from-go-to-rust
Another difference between rust and e.g. python is that rust expects you to invest more time to get code that’s runnable in the first place, but likely more well optimized and correct.
In my experience from writing rust, the language pushes you to write more efficient code compared to python because it makes things like copying visible and also because it’s easier to reason about memory usage compared to garbage collection which means that you’re more likely to have a useful model of the performance cost of various things while you’re programming.
It’s possible that a hypothetical lemmy written in python would have allowed the devs to do some big picture optimizations that they haven’t had the time to do yet in the rust version, so for the time being it might be slower than a python alternative.
Rust is likely to catch up though: eventually the rust version will probably also have this optimization while the python version has to resort to make smaller optimizations that the rust version already had in the first version of the code or that you get for free from the language.
I would like to point out that this article from Discord could be considered outdated these days. This comparison is using a old version of Go, that in recent years got a optimization on the GC and now would have much lower spikes than those showed in the article
Still, Rust surely will give you a higher performance and lower latency than Python
I mean, comparing it to Python is kinda unfair as Rust is closer to C and Python is one of the slowest languages out there. There is a whole spectrum of languages between Rust and Python. The final reason was probably that the devs were comfortable enough with Rust.
deleted by creator
Hi, programming.dev owner here. From what I’ve been seeing it’s a lot of memory issues. We were hitting swap which was causing massive disk io. You can see what happened with the disk io immediately after the upgrade to more memory.
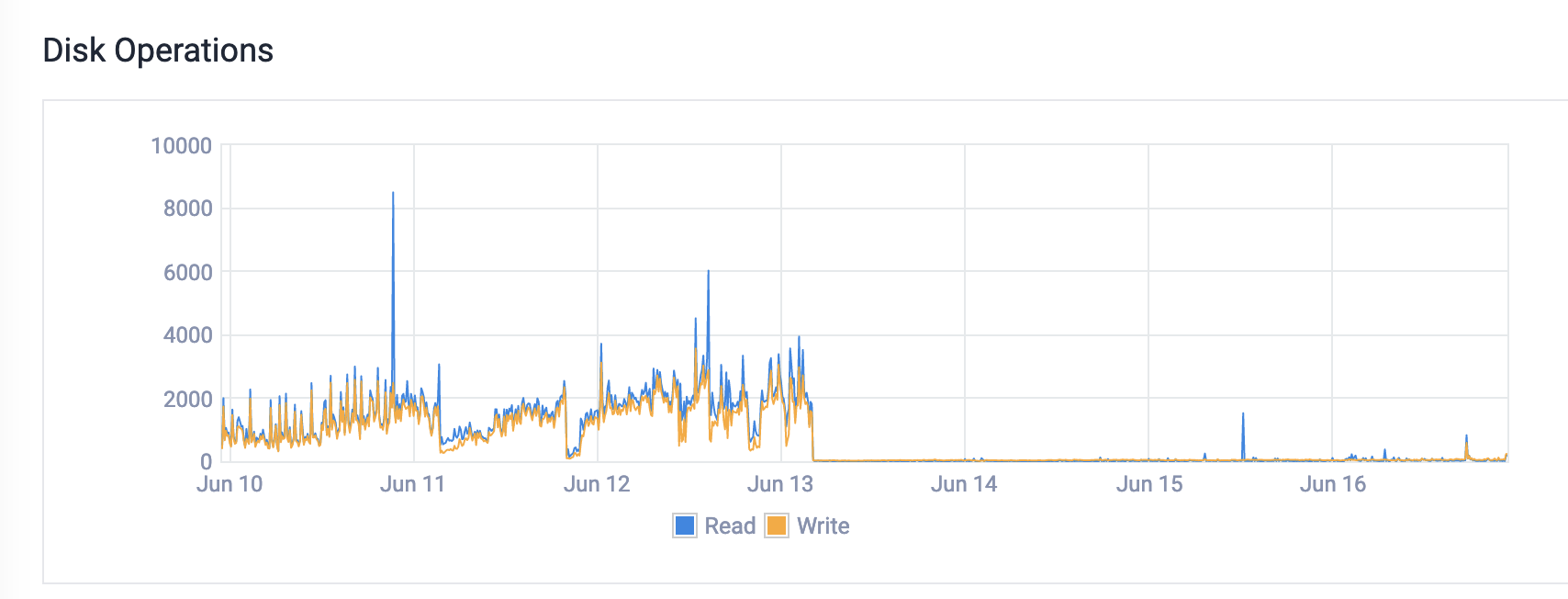 I know at least one reason is being resolved in this PR
I know at least one reason is being resolved in this PRWe were also having issues with the nginx config. There were some really weird settings that I don’t think were necessary. Finally, the federation is quite busy. So if someone subscribes to events from 10 different servers, we pull in every single event, even upvotes. There’s currently a lot of work being done around this stuff.
I don’t think Rust is the problem. I think it’s just a growth thing. Every platform has growth challenges, things grow in ways that you never expect. You might have thought that it was going to be IO constrained due to the federation, but in reality it’s memory constrained because memory is actually the most expensive thing to have on a server. etc.
So if someone subscribes to events from 10 different servers, we pull in every single event, even upvotes. There’s currently a lot of work being done around this stuff.
You mean like coalescing multiple events into a single message, or…? (I don’t know anything about ActivityPub, so apologies if this is a stupid question!)
correct. I’ve been looking for the thread to try and find it for you, but haven’t been having any luck. People have been discussing exactly that though, but it seems like it could cause some problems with vote faking. Anyway, it is being worked on!
Thank you for the insight. Fascinating. Also insane that ever upvote causes a flood of messages being distributed…
Its not code that seems to have difficulty scaling, it seems to be user curation and user trust that is being difficult to scale.
The lemmy.ml post that asks people to go elsewhere is still stickied and the first thing it mentions is that they have upgraded the server. So that does suggest that compute scaling is an issue.
It could also be an issue with disk i/o, data port throughput, database performance…
I mean, with all the server issues we’ve seen with the influx of users, it does seem like the code is difficult to scale
What makes you think that inefficient rust is slower than efficient Python? I mean, sure it could be possible if you are actively trying to make rust slow, but rust is multiple order of magnitude faster than python. If rust was to blame here then I don’t think any language could be fast enough.
Rust is not to blame, but that code that has been written in Rust might be to blame.
The algorithms used have more effect than the language used, and Rust might make using certain algorithms more painful and thus steer programmers towards less efficient algorithms. Using
cloneis often an example of this, it’s a little easier and gets around some borrow checker difficulties. (This is true in general, but I don’t know if this is what has happened with Lemmy.)Look at salvo [diesel] coming it at #200+ on this benchmark1, lots of programming languages have at least one framework that is faster on the microbenchmark. This isn’t especially meaningful, but it does show that, let’s say, a feature rich framework in Rust might end up being slower than a Python framework that’s laser focused on the specific use case.
What makes you think that inefficient rust is slower than efficient Python?
Well of course it can be. Performance issues are very often algorithmic rather than from execution efficiency.
Rust won’t make it slow for sure, but it’s not enough to ensure it’s fast.
When it comes to architecture I’m not a genius, but I think a lot of how federation works is tough.
Plus, even if you have a perfectly efficient backend it can only handle so much based on the hardware you’re running on. “Struggling to scale” can just mean “struggling to afford better hardware.”
I think threads like this one: https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=28440742 help explain the complexity of performance. There’s considerations from the development process, existing technology, simplicity, and more.
At this point I think the bottleneck is largely that every server has needed to upgrade for this wave of the reddit migration.
I’m not convinced using rust is all that useful for web development. There are already plenty of other mature well optimized solutions for backend web development that includes a lot of security, qol features ootb like mature orm’s with optimized database access which regardless of how fast your code is can bottleneck your site much faster if you don’t have smart database access.
Yeah, theoretically rust can be faster than ruby/python/node, but it’s harder to optimize it enough to get to that point and you will have a much harder time finding devs to work on such a project because the amount of backend devs that have enough rust experience is so small, they’re like on the opposite sides of the ven diagram of languages for web developers.
On top of all that, languages which are heavily used for web development often get low level optimizations baked into the frameworks/languages so you can get pretty amazing performance uplifts over time to bring it to the level of lower level languages.
Hear me out, but I believe that using Rust holds Lemmy back.
Writing Rust code is difficult, and fairly time consuming. It’s difficult to get right, and as other commenters have noted, Lemmy code seems to do a lot of things for the “hype factor” (like Websockets). It’s difficult to find enough devs as well.
The article about Discord switching to Rust from Go in the top comment is misleading in my opinion. They totally rearchitected their service while rewriting it, so it’s an apples to oranges comparision.
On the other hand, Rust is fairly resilient. The issues Lemmy is experiencing wouldn’t be fixed in Python vs Java, it’s more of an architectural constraint. Those issues, experienced devs can fix mostly regardless of language.
Ha! They are ditching Websockets in the next release. Good riddance.
But Rust is modern. The only real alternatives would be Go or Javascript, Go has a lot more footguns IMO, and Javascript has its own issues with the type system, etc.
The main issues you’re talking about are in the lemmy-ui which is not written in Rust, but in InfernoJS / Typescript.
Most every language in use gets pretty constant new releases so is effectively modern. So not sure why the criteria should be a hype language versus simply the best language for the job (performance level, dev time, dev availability, etc.).
I think you are getting things backwards… Learning to write rust might be hard, if you are not used to typed languages or languages with explicit memory management with stack/heap separation. However, writing rust is not hard. It might take slightly longer in the coding phase, since you are forced to do things correct, you need to handle errors and are not allowed to share data between threads in dangerous ways aso. But that makes the resulting software a lot better, which means that the testing and support is a lot less. So, if anything, the net result of writing software in rust is that it is easier, since you are not allowed to shoot your self in the foot over and over again.
And remember, that every time rust is making your life difficult, you might have introduced a subtle bug in another language.
If your college educated in cs, and your main issue with a codebase is the language its writen in, i have some serious questions as to how the hell you graduated
A rudimentary way to put it but ultimately correct.
Rust has already established itself as a solid language. That should be the first bell.
It’s difficult to get right
It is actually really easy. I wanted to rewrite my old rust coded that I did while I was learning it. But when I checked it after about year I have found that it was pretty decent.
Compiler really did help (actually more like clippy/rust-analyzer in that case).
Learning rust is hard, yeah. But I’ve found that once you get the hang of it, actually using rust and writing code day to day is as fast or faster than using other languages (Jacascript, Pythong, etc). Rust tells you exactly what you did wrong and why it’s dangerous, this is incredibly useful in avoiding bugs and speeds up productivity. Therefore, I have doubt the main creators of Lemmy have issues with writing rust code.
I agree that finding developers can be hard, though. Especially since rust is still a relatively new language. I also agree that new programmers who recently came to lemmy and want to help it succeed by contributing code will take a good bit of time to get to that point of ‘being comfortable enough with rust that it increases productivity’. However, I also think we have to consider the inverse, that the influx of new users will also see experienced rust programmers who want to help contribute to Lemmy and be successful at it (and in fact I think we’ve already seen this if I take Lemmy PR activity as any indication). Indeed even the rust subreddit stickied protest post hinted that rust developers are among the few who can help enact new alternative platforms to Reddit, and there are definitely OG and amazing programmers in that community.
That’s also not mentioning that rust has continued to gain traction and is continually one of the most favorite languages for devs (according to stackoverflow)
TL;DR: I’m a rust optimist and have faith in the rust community to help out Lemmy where it matters.
Source: been rust dev for 4+ years, do it for day job. Also considering helping out Lemmy when my life becomes a little bit less crazy
Lemmyrs/rustlang for rust instance btw
Whatever the performance bottlenecks are, I hope they can get them sorted so that any exponential growth caused by Reddit at the end of the month can be capitalized on.
I’ve got a feeling that other redditors who want to flee / branch out will look at these sites and so long as they see posts, comments and that it has a decent UI and loads well then people will stick around and build communities here.